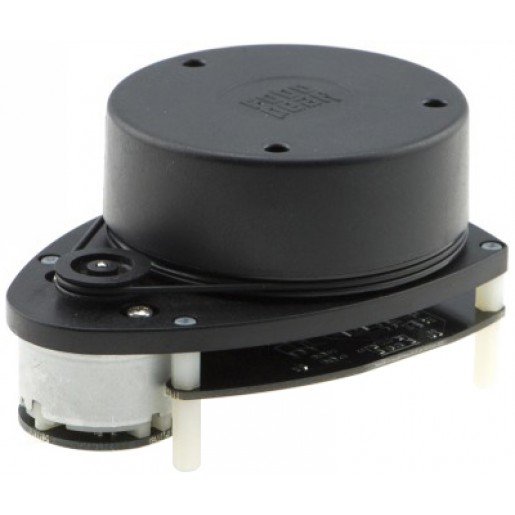
RPlidar overview
The RPlidar is a 360° SLAM-ready laser scanner. It is amongst the cheapest of its kind and yet, it offers accurated measures.
More info and where to find it: robotshop

RTabmap overview
RTabmap is a real-time RGB-D graph SLAM approach developped by M.Labbé and F.Michaud, from the IntRoLab.
More info and where to find: RTabmap official website
Mounting the RPlidar on the turtlebot
First, you have to physically mount the laser on your turtlebot. Get your drill, a screwdriver and screw it on an empty plate! I fixed mine just above the kinect:
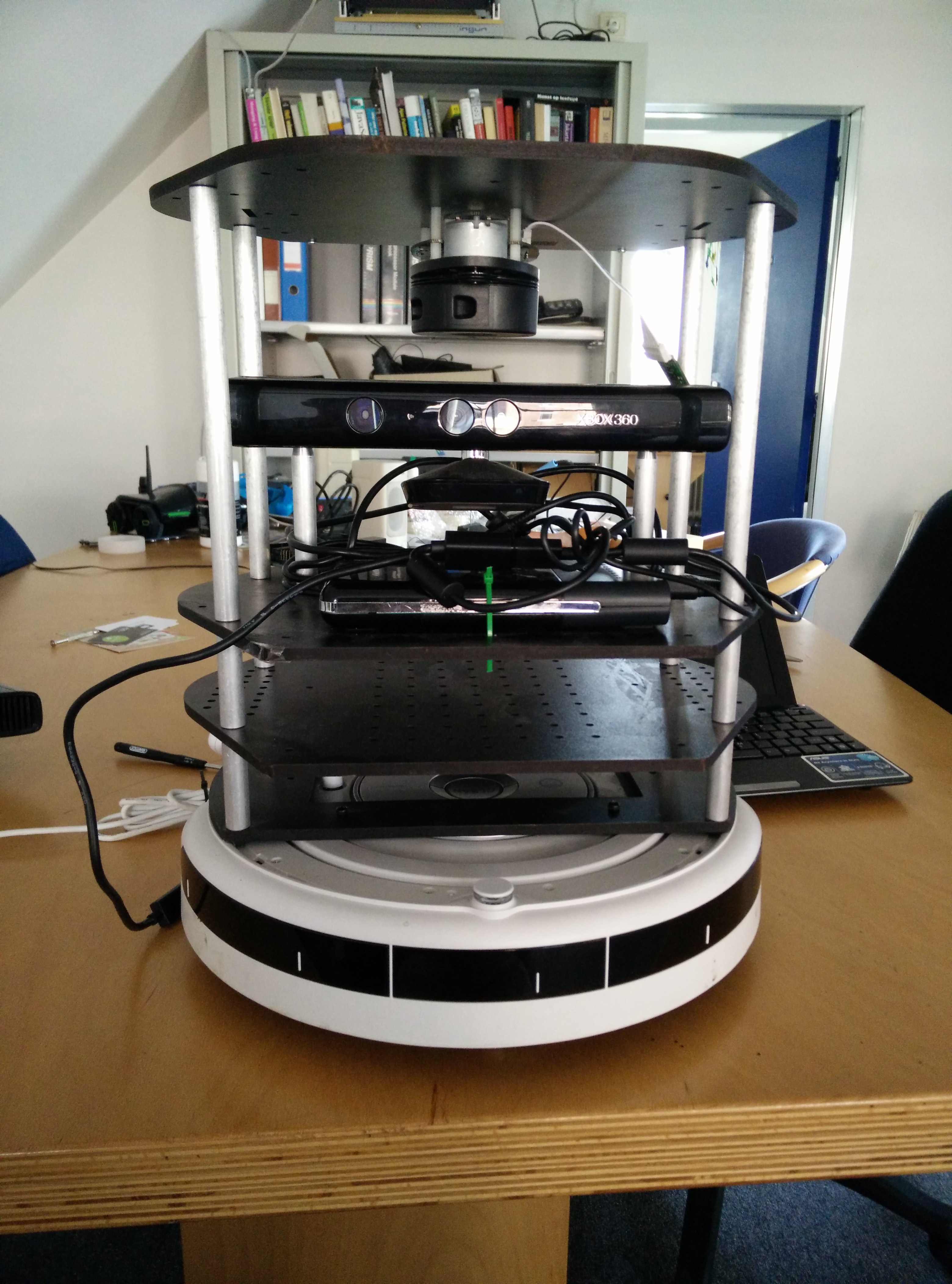
The next step is to update your turtlebot’s description files to include the laser. We need to find which plate is the laser fixed to:
roscd turtlebot_description/urdf/stacks
gedit circles.urdf.xacro
In my case, it was:
<joint name="plate_3_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="-0.01316 0 0.2063496" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="plate_2_link"/>
<child link="plate_3_link" />
</joint>
How to find it: the plate_3 was 20cm above plate_2 so I knew parent link=plate_2_link and Z=~0.20 Then, we need to adjust the position of the laser relative to its plate.
roscd turtlebot_create/../create_description/urdf
gedit create.urdf.xacro
Modify: (coordinates in meters of the center of the rotating part of the laser, rotations in radians.)
<joint name="laser_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="[PositionX] [PositionY] [PositionZ]" rpy="[rotation/X] [rotation/Y] [rotation/Z]" />
<parent link="[plate on which the laser is]" />
<child link="laser" />
</joint>
visualize Turtlebot on rviz to make sure your parameters are good, open two terminals and start:
roslaunch turtlebot_bringup minimal.launch
rosrun rviz rviz
in rviz: add -> robot model (you may have to change the fixed frame to base_link) You should see something like this:
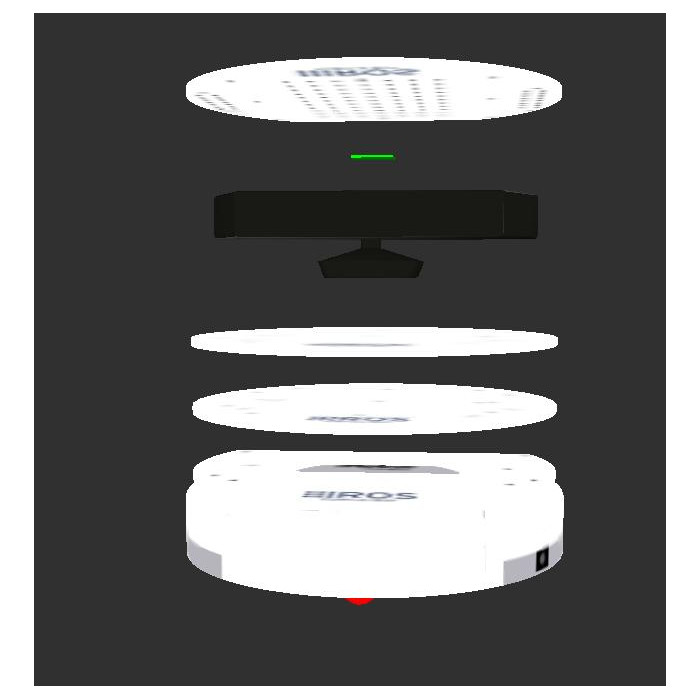

Where the green rectangle represent the RPlidar.
Installing ROS packages for the RPlidar
I installed it from source, which you can find here: https://github.com/robopeak/rplidar_ros
cd catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/robopeak/rplidar_ros.git rplidar
cd ..
catkin_make
source devel/setup.bash
You may have to change the ttyUSBX defined in rplidar.launch to have it working with along the turtlebot.
roscd rplidar_ros/launch
gedit rplidar.launch
Configuring the turtlebot launch file
Now, we want to generate the scan topic from the RPlidar and the kinect to compare them with RTabmap. Therefore, we have to change the name of the scan topic from the kinect.
roscd turtlebot_bringup/launch
gedit 3dsensor.launch
change
<!-- Laserscan topic -->
<arg name="scan_topic" default="scan"/>
to
<!-- Laserscan topic -->
<arg name="scan_topic" default="scan_kinect"/>
Configuring RTabmap launch file
Now that we have a working rplidar publishing on /scan and a kinect publishing an emulated scan on /scan_kinect, we have to modify our rtabmap launch file to include one or another. The easiest and most convenient way is to define an argument scan_topic which can be either /scan or /scan_kinect.
Edit your favorite launch file this way (e.g. rgbd_mapping.launch):
roscd rtabmap_ros/launch
gedit rgbd_mapping.launch
Add this line under the other arguments:
<arg name="scan_topic" default="/scan"/>
then change the line remapping the scan_topic in the visual SLAM and the visulation node to
<remap from="scan" to="$(arg scan_topic)"/>
Make sur you have set the subscribe_laserScan to true in those nodes:
<param name="subscribe_laserScan" type="bool" value="true"/>
Now your turtlebot is ready to use rtabmap with one or the other laser ! By default it will use the RPlidar, if you want to start rtabmap with the kinect laser, use this line:
roslaunch rtabmap_ros rgbd_mapping.launch scan_topic:=/scan_kinect
RPlidar vs kinect laserscan
In order to compare both methods in the exact same conditions, we have to record our ros_topic during the run, and provide those recorded runs to rtabmap.
To record them as a rosbag:
cd bagfiles
rosbag record -O turtlebotrun /tf /odom /camera/depth_registered/camera_info /camera/depth_registered/image_raw camera/rgb/camera_info /camera/rgb/image_rect_color /scan /scan_kinect
To play the recorded bagfile:
rosbag play turtlebotrun --clock
Here is an example of run. This is what the room we used look like I.R.L.:
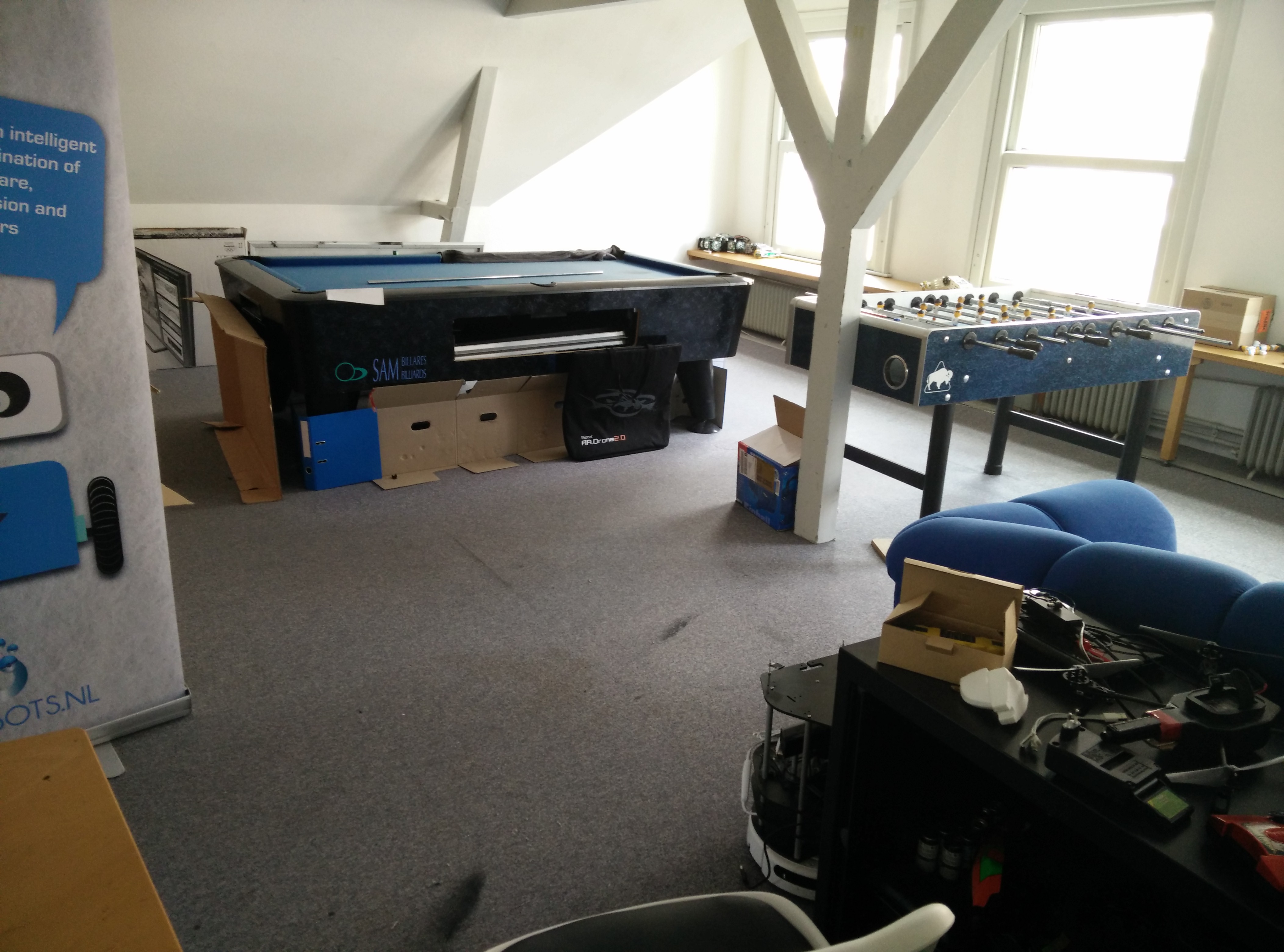
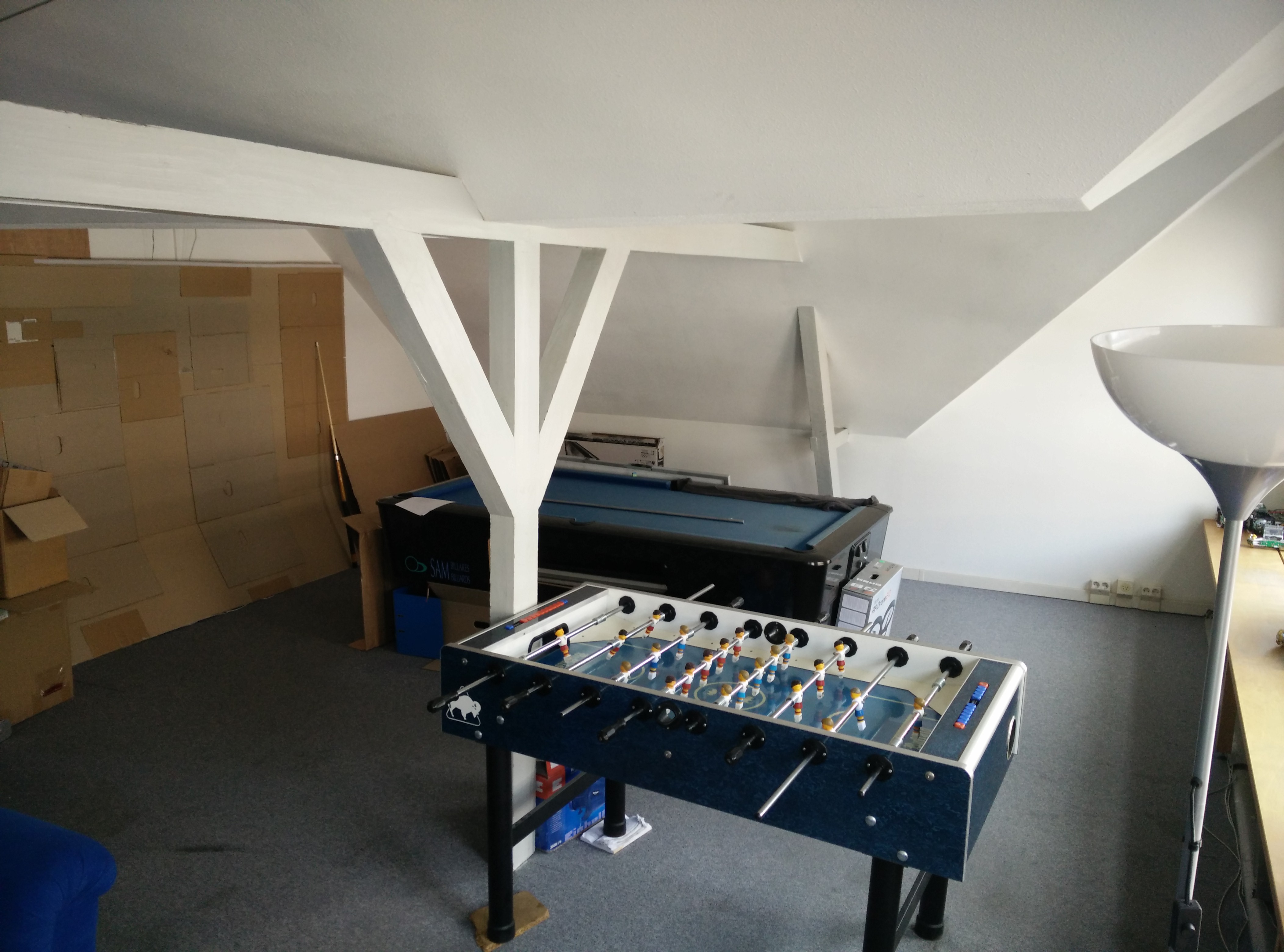


Turtlebot ran around the pool table. The RTabmap run footage: (The multicolor voxels represent the rplidar scan)
Here are the two point clouds extracted from the laser scan and the kinect laser scan during a the fast run showed above:
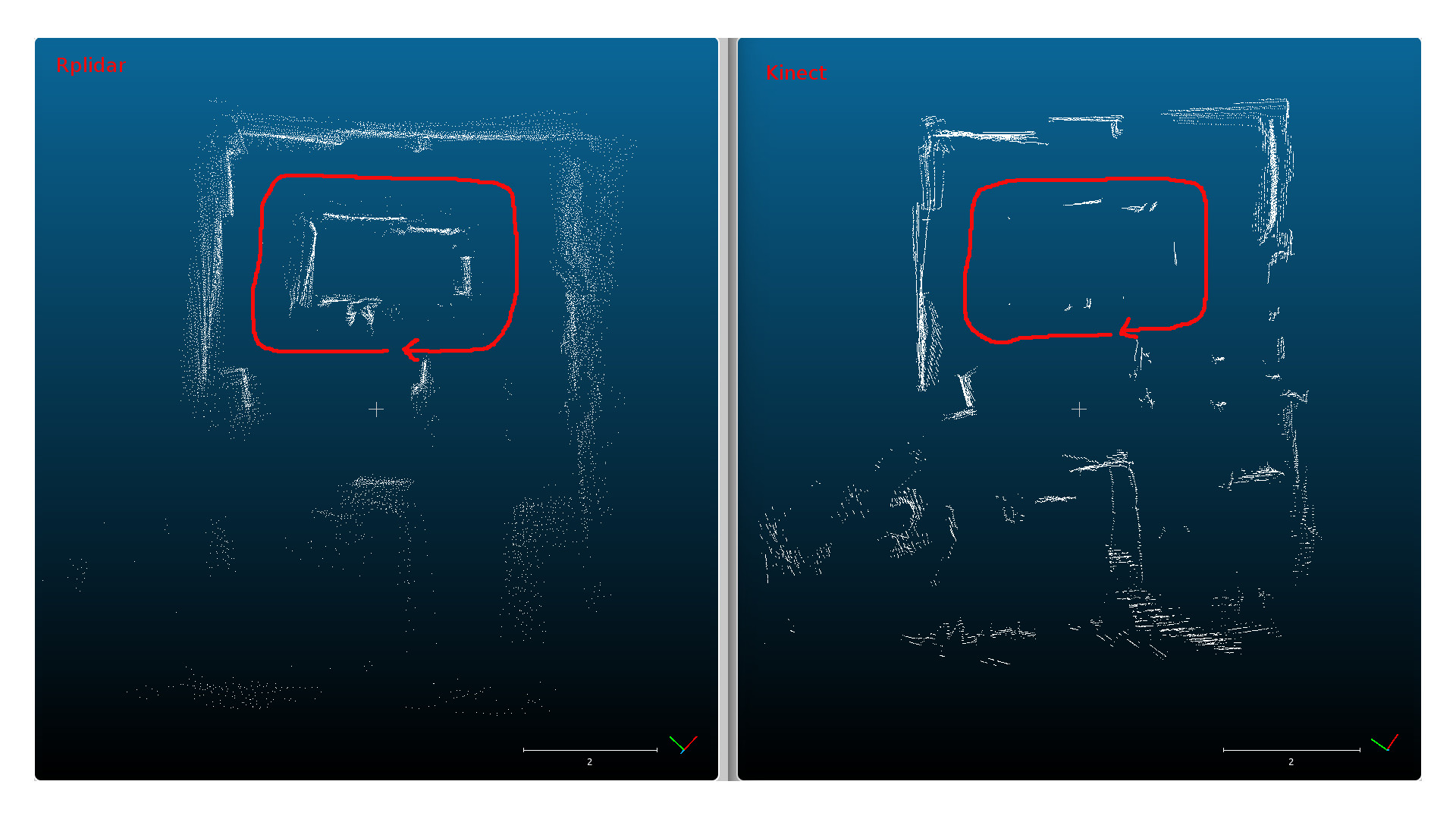
The red line is the path followed by the turtlebot. As we can see, the results are similar except that the pool table is detected with the rplidar and not the kinect, because it was not in the kinect’s field of vision.
The graphview (occupancy grid) made from rtabmap looks like this:
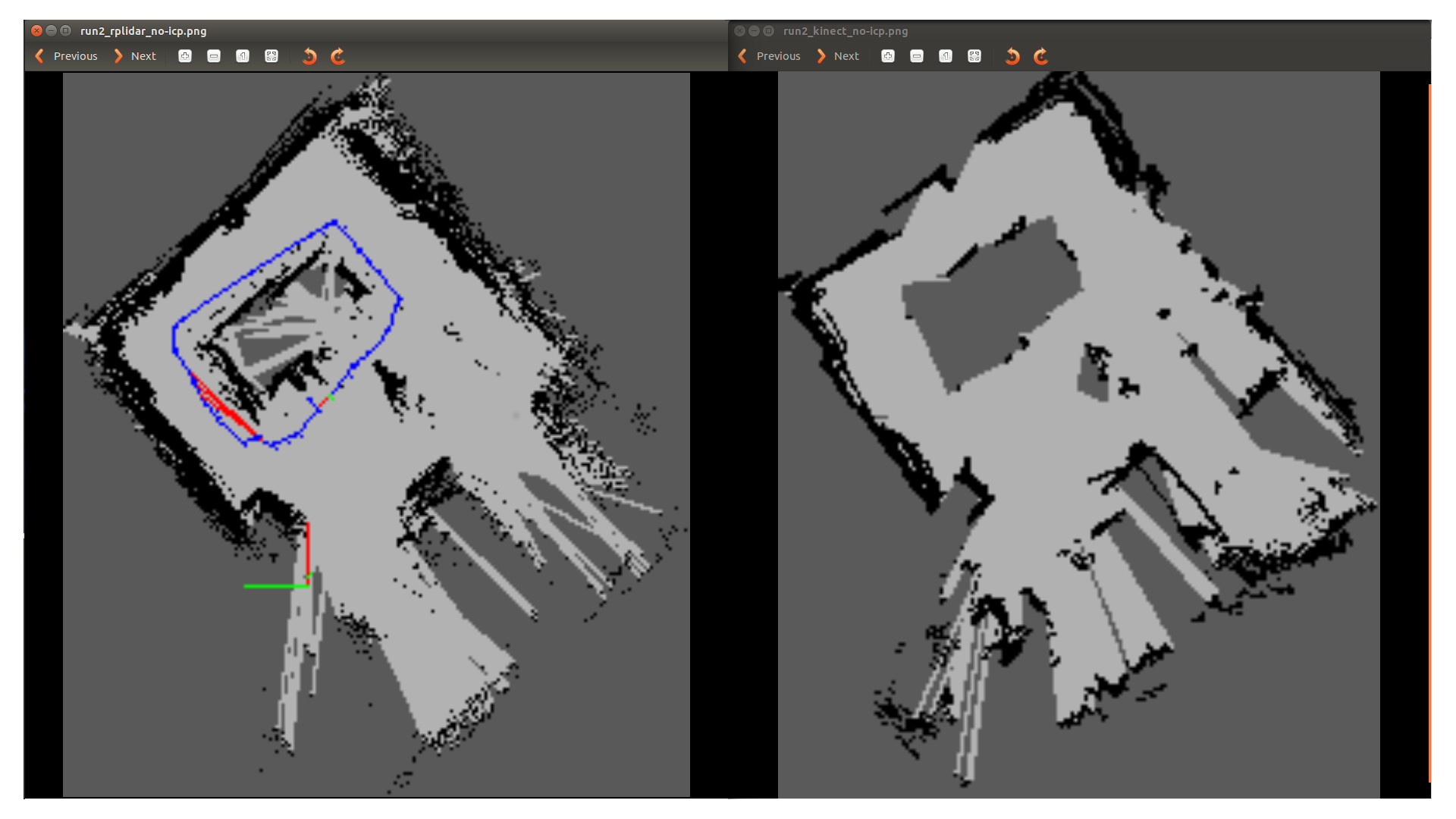
A few details about the zone: There were some holes in the cardboard around the pool table. This is why the pool table is partially filled in the rplidar scan. Also, the mess on the top corner on both screen is due to the presence of a radiator.
To compare both maps, we used different criterias such as the number of missing walls, the unknown surface in known area, the straightnes of the walls… We evaluated that, on a short run, the rplidar gave better result. Its wider range gives him more information and we don’t have to look in every direction to map the area. However, if we did so, the results were similar with the kinect. But in a real environment, and depending to the exploration algorithm used, we are more likely to be in a “fast-run” setup.
blog comments powered by Disqus
